Geography of Madagascar
The island nation of Madagascar is located in the Indian Ocean and occupies an important position along the Mozambique Channel. It is also the fourth largest island in the world. Madagascar Geography includes information pertaining to the various landforms, rivers, climate, natural resources, flora and fauna of the island.
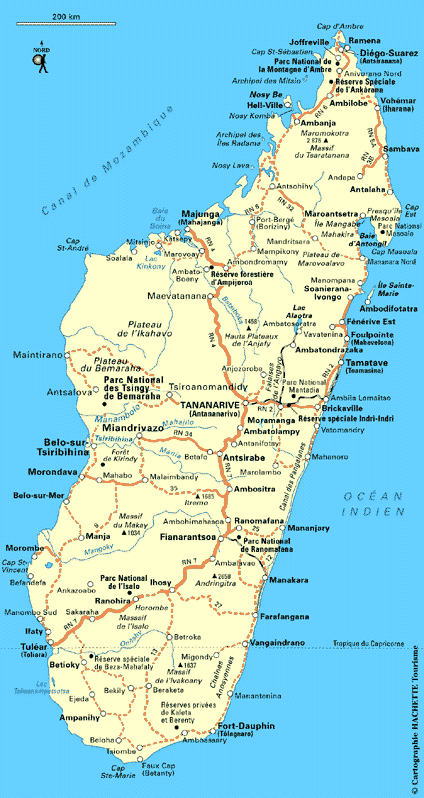
Madagascar stretches over a total area of 587,040 square kilometers of which 581,540 square kilometers is land area and the remaining 5,500 square kilometers is taken up by the various water bodies. The island is narrow along the coastal area, whereas, the mountains and plateaus occur in the central part. Maromokotro is the highest peak at an elevation of 2,876 meters. The topography of the island is broadly divided into five main regions, namely, the central highlands, the east coast, the southwest part, the east coast and the Tsaratanana Massif.
Major Rivers and Lakes of Madagascar:
The rivers of Madagascar include Ihosy, Mania, Onilahy, Mangoky and Betsiboka. Madagascar Rivers also include some rivers like Mangoro, Maningory, Mananara and others, which originate in the central highlands and flow towards the eastern coast. Apart from them, rivers like Ivondro, Mananjary and Bemarivo also flow eastwards and fall into the Indian Ocean. The courses of these Madagascar Rivers are short as the water parting is situated on the eastern coast itself. The rivers flow with great speed and often give rise to waterfalls as they encounter sharp gradients.
The Major rivers of Madagascar include:
Mangoro
Maningory
Mananara
Ivondro
Mananjary
These rivers of Madagascar drain the flood plains making them fertile for agriculture.
Lakes:
There are quite a few lakes in Madagascar. Lake Alaotra is the largest of them all. Apart from Lake Alaotra, the other Madagascar lakes include Lake Kinkony, Lake Tritiva, Lake Ihotry, Lake Tsimanampetsotsa and others. These lakes in Madagascar make the country beautiful.
Situated in the Toamasina region, Lake Alaotra is the largest of the Madagascar lakes. It extends over an area of 900 square kilometers .The Lake is extensively used for the purpose of fishing and is at the same time the home to diverse varieties of flora and fauna like the Alaotra Gentle Lemur and five of the endangered species of fishes. A large number of marshes, rice fields and other wetlands are also found in the surroundings. In fact the region yields the maximum productivity as far as rice is concerned. The hills encircling the lake were covered with dense forests .But continued and random deforestation has left the slopes barren.
Lake Kinkony lies in the north western portion of the country and occupies an area of about 100 square kilometers. The environs of the lake are an important habitat for several species of birds. It also occupies a major place among the lakes in Madagascar.
Lake Tritiva is said to have formed at a place where there was the presence of a crater while Lake Ihotry is located in the south western region of the country .This part of the country is a semi desert and the lake water is high on salinity content.
Lake Tsimanampetsotsa lies in the southwestern Toliara region of the country and is one of the major Madagascar lakes. The lake and its surrounding area are listed by the Ramsar Convention as one of the important wetland areas .The surface area of the lake spans almost 456 square kilometers and is one of the saline lakes of the province.
Climate of Madagascar:
Climate of Madagascar is basically tropical but varies across the region. It becomes temperate as one move inland while further down south it becomes all the more arid. The southeastern trade winds that are formed in the Indian Ocean greatly influence the climate of Madagascar. The Madagascar climate offers two distinctive seasons in the country. The summer months last from November to April and are disrupted by occasional rains. The period between May and October is characterized by a comparatively cool climate.
The eastern coast of the island gets the maximum amount of rainfall owing to its exposure to the trade winds and has to face cyclonic conditions frequently. The central highlands are more or less on the drier side because of its elevation. Regular thunderstorms are characteristic of the central highlands during the monsoons and frequent lightning also pose serious threats.
The capital of Madagascar, Antananarivo, receives its maximum share of rainfall between November and April. The period between May and October is warm and enjoyable. However, it can be a bit cold in the morning. The sky at this time of the year remains clear and looks really beautiful.
In comparison to the other regions of Madagascar, the western coast remains dry for most parts of the year. The trade winds, by the time they arrive in this part, lose out on the moisture content. As a result, the southern and south western halves of the island are arid. These barren lands receive minimum amount of rainfall and can be termed as semi deserts. Surface water is found mostly on the eastern coast and in the northern territories of the island.
The Madagascar islands have to bear the brunt of cyclones within regular intervals of time. The cyclones inflict huge losses of life and property. Yet, the climate of Madagascar mostly remain favorable for the tourists who to visit the country come from different parts of the world.
Ecology of Madagascar:
Ecology of Madagascar is extraordinarily rich as the island is a hub of numerous endemic species and unique plants. The island has about 85 percent of such plants and animals, which are found nowhere else in the planet. Located at the off coast of Africa, Madagascar ecosystem has variety of climatic zones including tropical and temperate climates. The Madagascar ecology is somewhat distinct from others as the island was isolated from Africa millions of years ago, thus carrying numerous unique species with it. With the passage of time these species began to diverge from their ancestors of the mainland and they started possessing different genetic traits in an entirely unique Madagascar ecosystem.
The geography of Madagascar along with its long isolation contributed to the formation of the island's unique ecosystem. The climatic factors in Madagascar also diverged and the isolated island had its own climatic variations. The climatic factors were also responsible for huge varieties of plant and animal species to survive in this island. The ecology of Madagascar is colorful with about 50 species of lemurs, 250 species of birds and about 245 species of reptiles that are endemic to the island. Madagascar has about 80 percent of unique flowering plants along with several rare orchid species found nowhere else in the world.
The ecology of Madagascar is blessed with great climatic factors which support rich vegetation and agriculture and Madagascar is presently the world's great conservation priorities. The variation in Madagascar ecology is based on certain factors like its relatively large size tropical location along with the late arrivals of human beings to this isolated island.
Ecology of Madagascar is diverse because the island was isolated for a long period. Thus many plant and animal species found in the African mainland are also not found over here. Paleontologists have done extensive research on Madagascar ecology. Mesozoic era deposits claimed that dinosaurs, mammals and early birds once inhabited this isolated island.
Flora and Fauna:
Flora and fauna in Madagascar is extremely popular as the island home for some of the most unique and rare species of the world. Numerous species of plants, reptiles, insects and fishes are found exclusively in this island, and they are the very heart of Madagascar geography. Initially Madagascar was blanketed by forests but later on deforestation caused a huge devastation of these natural assets of the island.
A large portion of the Madagascar inhabits the rain forests of the island. The rain forests mainly consist of numerous unique plant species and the island houses about 900 species of orchids. Coconut, bananas, mangoes, vanilla and other tropical plants are widespread in Madagascar forests.
Some of the unique flora of Madagascar is mentioned below:
The Alluaudia Procera
The Rosy Periwinkle
The Aloe Vaombe
The Euphorbia Viguieri
The Moist Cucurbitaceae
The Adansonia Grandidieri
Fauna is an equally important part of the Madagascar Island and the lemurs and the chameleons can be considered to be the dual iconic vertebrates of Madagascar. The island has numerous varieties of these two species and it is quite easy to spot them. The wild life safari is the best bet to explore these friendly wild creatures of the island. The parks and reserves of Madagascar offer numerous varieties of lemurs and they are really the most striking among other wild life species.
Natural Resources in Madagascar:
The natural resources found in Madagascar are basically graphite, coal, chromate, bauxite, semiprecious stones, salt, tar sands, mica, hydro-power and fish. Madagascar is blessed with the great forestry and they in turn are the producers of various natural products.
Mining of natural resources is an integral part of the economy generated by the natural resources at Madagascar. The mining industry of Madagascar exports almost all the Madagascar natural resources, and the island was ranked as the 10th largest producer of chromate in 1999.
